|
Creatine What is Creatine?
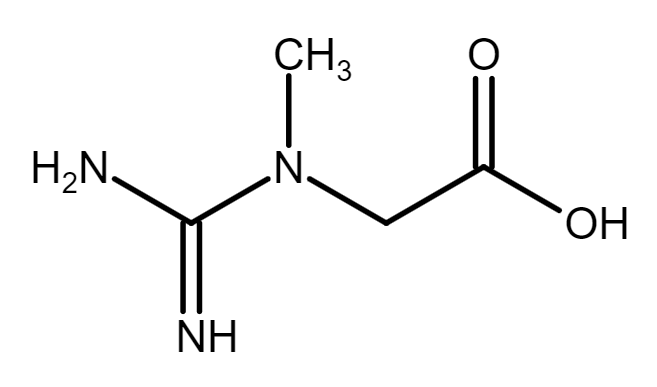
Creatine is a popular dietary supplement that is commonly used by athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts to improve their physical performance. Creatine is closely related to ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary source of energy for muscle contractions during exercise. When you exercise, your muscles use ATP to generate energy for movement. However, the amount of ATP stored in your muscles is limited, and it is quickly depleted during intense exercise. This is where creatine comes in. Creatine is converted into phosphocreatine in the muscles, which can add a phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) to form ATP. This means that creatine can help to replenish the ATP stores in your muscles, allowing you to maintain high-intensity exercise for longer periods of time. By increasing the availability of ATP in your muscles, creatine supplementation can improve athletic performance, increase muscle strength and size, and enhance recovery after exercise. It is important to note that the benefits of creatine supplementation may vary depending on the individual, their training program, and their diet. Overall, creatine is a safe and effective supplement that can be a useful tool for athletes and fitness enthusiasts looking to improve their performance and achieve their goals. As with any supplement, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional before starting creatine supplementation. What are the benefits of Creatine? Here are some of the benefits of creatine: 1. Increases muscle strength: Creatine can help increase muscle strength by improving the availability of energy to the muscles during intense exercise. 2. Enhances athletic performance: Creatine supplementation has been shown to improve performance in activities that require short bursts of intense energy, such as weightlifting, sprinting, and jumping. 3. Increases muscle size: Creatine can help increase muscle size by promoting the retention of water in muscle cells, which can lead to greater muscle volume and improved muscle definition. 4. Improves recovery: Creatine can help reduce muscle damage and promote faster recovery after exercise, which can allow athletes to train harder and more frequently. 5. May have neuroprotective effects: Some research suggests that creatine may have neuroprotective effects and may be beneficial for people with certain neurological conditions. There is some evidence to suggest that creatine may have neuroprotective abilities. Creatine is involved in the production of ATP, which is the primary source of energy for all cells in the body, including brain cells. By increasing ATP production in the brain, creatine may help to protect neurons from damage and improve cognitive function. Several studies have investigated the potential neuroprotective effects of creatine in various neurological conditions, including Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and traumatic brain injury. While the results are not conclusive, some studies have suggested that creatine supplementation may help to improve motor function, reduce inflammation, and protect against oxidative stress in the brain. One proposed mechanism for the neuroprotective effects of creatine is its ability to increase the availability of phosphocreatine in the brain. Phosphocreatine can act as an energy buffer in the brain, helping to maintain ATP levels and protect neurons from damage. It is important to note that the research on creatine's neuroprotective abilities is still in the early stages, and more studies are needed to fully understand its potential benefits. Additionally, creatine supplementation may not be appropriate for everyone, and it is always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. Should I take Creatine? That's a good question and more commonly asked by women. The short answer is yes, probably, you should consider taking creatine daily. Creatine can cause a short term weight gain due to increased muscle volume but this isn't body fat and is a benefit to you and your body. Creatine doesn't benefit everyone. Some people already have considerable creatine stores and adding more daily creatine doesn't produce any benefit. However, the benefits of creatine aren't something you can feel or measure so it's unlikely you will know if its benefiting you specifically. Considering it's high level of safety and potential benefits beyond just sports we feel it's worth considering adding to your daily regime. Just taking 3-5g daily, no need to back load or anything. You only need monohydtate, any other type doesn't have more benefit but typically costs more and may actually have side effects. You also don't need to purchase any specific brands, creatine monohydrate is just creatine monohydrate. Its tasteless so just add it to yogurt or oats or a shake. You can take it whenever is best for you each day, there's no benefit from its timing Are there side effects? Some people can get stomach cramps in rare cases. please ensure you hydrate well and this shouldn't happen. Other possible side effects are below but are typically rare:
If you have liver function issues or diabetes we recommend not taking creatine. *Always consult your MD if unsure. Comments are closed.
|
AuthorI'm Paul Leonard, CEO & founder of PLT Nutrition. Categories
All
|
|
Current PLT Members
|
Quick Links
|
Connect With Us
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed